(E)-2-氨基-4-甲基-5-膦酰基-3-戊烯酸
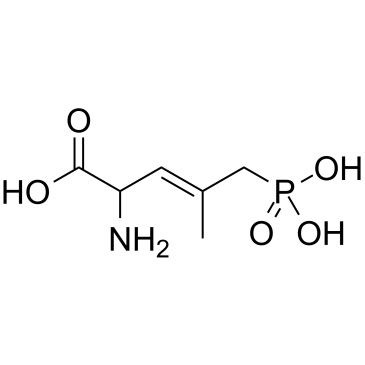
(E)-2-氨基-4-甲基-5-膦酰基-3-戊烯酸结构式

|
常用名 | (E)-2-氨基-4-甲基-5-膦酰基-3-戊烯酸 | 英文名 | CGP 37849 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS号 | 127910-31-0 | 分子量 | 209.13700 | |
| 密度 | 1.506 g/cm3 | 沸点 | 523.1ºC at 760 mmHg | |
| 分子式 | C6H12NO5P | 熔点 | N/A | |
| MSDS | 中文版 美版 | 闪点 | 270.2ºC | |
| 符号 |

GHS07 |
信号词 | Warning |
|
Involvement of voltage- and ligand-gated Ca2+ channels in the neuroexcitatory and synergistic effects of putative uremic neurotoxins.
Kidney Int. 63(5) , 1764-75, (2003) Renal failure has been viewed as a state of cellular calcium toxicity due to the retention of small fast-acting molecules. We have tested this hypothesis and identified potentially neuroexcitatory compounds among a number of putative uremic neurotoxins by exa... |
|
|
GSA: behavioral, histological, electrophysiological and neurochemical effects.
Physiol. Behav. 84(2) , 251-64, (2005) Renal insufficient patients suffer from a variety of complications as direct and indirect consequence of accumulation of retention solutes. Guanidinosuccinic acid (GSA) is an important probable uremic toxin, increased in plasma, urine, cerebrospinal fluid and... |
|
|
Competitive NMDA receptor antagonists and agonists: effects on spontaneous alternation in mice exposed to cerebral oligemia.
Pol. J. Pharmacol. 56(1) , 59-66, (2004) The purpose of the present study was to investigate the effects of competitive NMDA receptor antagonists,D,L-(E)-2-amino-4-methyl-5-phosphono-3-pentenoic acid (CGP 37849) and its ethyl ester (CGP 39551), or agonist, N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) on spontaneous ... |
|
|
CGP 37849 and CGP 39551: novel competitive N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor antagonists with potent oral anticonvulsant activity.
Prog. Clin. Biol. Res. 361 , 421-7, (1990)
|
|
|
NMDA/glutamate mechanism of magnesium-induced anxiolytic-like behavior in mice.
Pharmacol. Rep. 60(5) , 655-63, (2008) The anxiolytic-like activity of magnesium in mice during the elevated plus maze (EPM) has been demonstrated previously. In the present study, we examined the involvement of NMDA/glutamate receptor ligands on the magnesium effect on the EPM. We demonstrated th... |
|
|
Impact of postnatal blockade of N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors on rat behavior: a search for a new developmental model of schizophrenia.
Neuroscience 153(4) , 1370-9, (2008) The malfunction of glutamatergic neurotransmission in the neonatal or postnatal periods may be a risk factor for the appearance of neuroanatomical, neurochemical or functional changes that are characteristic of schizophrenia. Thus, the present study was under... |
|
|
Combined treatment with NMDA antagonist, CGP 37849, and sigma receptor agonists, SA4503 or DTG, decreases the neuroleptic-induced catalepsy in rats.
Pol. J. Pharmacol. 52(4) , 313-6, (2000) The obtained results indicate that joint administration of CGP 37849, a competitive NMDA receptor antagonist, and SA4503, a sigma1 (sigma1) receptor agonist or DTG, sigma 1/2 receptor agonist, evoked anticataleptic effect at doses which were ineffective when ... |
|
|
Blockade of NMDA receptors in postnatal period decreased density of tyrosine hydroxylase immunoreactive axonal arbors in the medial prefrontal cortex of adult rats.
J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 56(2) , 205-21, (2005) Malfunction of glutamatergic neurotransmission in postnatal period is considered to be a risk factor for development of schizophrenia. Thus, the present study investigates the impact of NMDA receptor blockade in the postnatal period on the density of tyrosine... |
|
|
Functional roles of NMDA receptor NR2A and NR2B subunits in the acute intoxicating effects of ethanol in mice.
Synapse 56(4) , 222-5, (2005) The present study examined the roles of NR2A and NR2B subunit-containing NMDA receptors in the mediation of the sedative/hypnotic effects of ethanol in mice. The ability of the competitive NMDA antagonist, CGP-37849 (0, 1, or 3 mg/kg), and the NR2B-selective ... |
|
|
Detrimental effect of postnatal blockade of N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors on sensorimotor gating is reversed by neuroleptic drugs.
Pharmacol. Rep. 60(6) , 856-64, (2008) Postnatal hypofunction of N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptors leads to several behavioral deficits in adult rats resembling deficits typical of schizophrenia-like deficits of sensorimotor gating. Thus far, it is not known whether the above disruptions are s... |