花生四烯酸
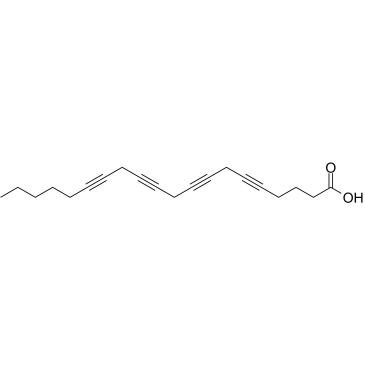
花生四烯酸结构式

|
常用名 | 花生四烯酸 | 英文名 | 5,8,11,14-Icosatetraynoic acid |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS号 | 1191-85-1 | 分子量 | 296.403 | |
| 密度 | 1.0±0.1 g/cm3 | 沸点 | 490.3±45.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| 分子式 | C20H24O2 | 熔点 | 79-81ºC | |
| MSDS | 中文版 美版 | 闪点 | 226.6±23.4 °C |
|
Arachidonic acid induces brain endothelial cell apoptosis via p38-MAPK and intracellular calcium signaling.
Microvasc. Res. 98 , 145-58, (2015) Arachidonic acid (AA), a bioactive fatty acid whose levels increase during neuroinflammation, contributes to cerebral vascular damage and dysfunction. However, the mode of injury and underlying signaling mechanisms remain unknown. Challenge of primary human b... |
|
|
High extracellular Ca2+ stimulates Ca2+-activated Cl- currents in frog parathyroid cells through the mediation of arachidonic acid cascade.
PLoS ONE 6(4) , e19158, (2011) Elevation of extracellular Ca(2+) concentration induces intracellular Ca(2+) signaling in parathyroid cells. The response is due to stimulation of the phospholipase C/Ca(2+) pathways, but the direct mechanism responsible for the rise of intracellular Ca(2+) c... |
|
|
Reactive oxygen species mediate arachidonic acid-induced dilation in porcine coronary microvessels.
Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 285(6) , H2309-15, (2003) Reactive oxygen species (ROS) have been proposed to mediate vasodilation in the microcirculation. We investigated the role of ROS in arachidonic acid (AA)-induced coronary microvascular dilation. Porcine epicardial coronary arterioles (110 +/- 4 microm diamet... |
|
|
Possible mediators of connecting tubule glomerular feedback.
Hypertension 53(2) , 319-23, (2009) In the renal cortex, the connecting tubule (CNT) returns to the glomerular hilum and contacts the afferent arteriole (Af-Art). Increasing Na delivery to the CNT dilates the Af-Art by activating epithelial Na channels, a process that we call connecting tubule ... |
|
|
A role for phospholipase A in auxin-regulated gene expression.
FEBS Lett. 581(22) , 4205-11, (2007) Auxin increases phospholipase A(2) activity within 2min (Paul, R., Holk, A. and Scherer, G.F.E. (1998) Fatty acids and lysophospholipids as potential second messengers in auxin action. Rapid activation of phospholipase A(2) activity by auxin in suspension-cul... |
|
|
Probing conformational changes in lipoxygenases upon membrane binding: fine-tuning by the active site inhibitor ETYA.
Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1841(1) , 1-10, (2014) Lipoxygenases (LOXs) are lipid-peroxidizing enzymes that are involved in the metabolism of polyunsaturated fatty acids. Their biological activity includes a membrane binding process whose molecular details are not completely understood. The mechanism of enzym... |
|
|
Capsazepine, a vanilloid antagonist, abolishes tonic responses induced by 20-HETE on guinea pig airway smooth muscle.
Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell. Mol. Physiol. 288(3) , L460-70, (2005) The aim of this study was to delineate the mode of action of 20-hydroxy-eicosatetraenoic acid (20-HETE) in airway smooth muscle (ASM) cells. ASM metabolizes arachidonic acid by various enzymatic pathways, including the cytochrome P-450 (CYP-450) omega-hydroxy... |
|
|
Identification and localization of an arachidonic acid-sensitive potassium channel in the cochlea.
J. Neurosci. 24(28) , 6265-76, (2004) Receptor cells of the auditory and vestibular end organs of vertebrates acquire various types of potassium channels during development. Their expression and kinetics can differ along the tonotopic axis as well as in different cell types of the sensory epithel... |
|
|
Arachidonic acid modulates Na+ currents by non-metabolic and metabolic pathways in rat cerebellar granule cells.
Biochem. J. 438(1) , 203-15, (2011) AA (arachidonic acid), which possesses both neurotoxic and neurotrophic activities, has been implicated as a messenger in both physiological and pathophysiological processes. In the present study, we investigated the effects of both extracellular and intracel... |
|
|
Complex expression and localization of inactivating Kv channels in cultured hippocampal astrocytes.
J. Neurophysiol. 93(3) , 1699-709, (2005) Voltage-gated potassium channels are well established as critical for setting action potential frequency, membrane potential, and neurotransmitter release in neurons. However, their role in the "nonexcitable" glial cell type is yet to be fully understood. We ... |