Microencapsulation of caffeine loaded in polysaccharide based delivery systems
Nairah Noor, Asima Shah, Asir Gani, Adil Gani, F.A. Masoodi
文献索引:10.1016/j.foodhyd.2018.04.001
全文:HTML全文
摘要
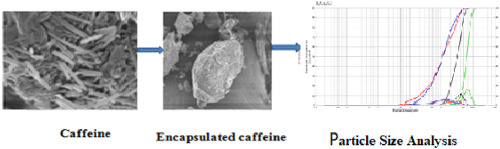
Encapsulation of caffeine in different polysaccharide materials (β-glucan, resistant starch, and β-cyclodextrin) by freeze drying technique to form caffeine loaded microparticles and determine their morphological, structural, and steady release behavior in simulated gastrointestinal (GI) conditions was studied. Swelling index of β-glucan and resistant starch was observed highest at pH 3 whereas at pH 6.5 swelling index decreased significantly (p ≤ 0.05). The morphology of the particles was characterized using SEM. The peaks at 1700 cm−1, 950 cm−1 and 1300-1350 cm−1 confirm the presence of caffeine in encapsulated wall materials as shown by FTIR. DSC analysis revealed decrease in peak melting temperature of caffeine loaded microparticles. The particle size distribution revealed largest size of 297.553 μm for resistant starch and smallest mean particle size of 95.17 μm corresponding to that of β-cyclodextrin whereas the highest encapsulation efficiency (98%) was observed in β-glucan. β-glucan showed maximum decline in the release of caffeine followed by resistant starch and β-cyclodextrin under mimicked stomach conditions whereas RS provided more slow release in intestinal conditions.
|
Physicochemical, textural, rheological and microstructural p...
2018-04-03 [10.1016/j.foodhyd.2018.04.008] |
|
High Internal Phase Emulsions Stabilized by Starch Nanocryst...
2018-04-03 [10.1016/j.foodhyd.2018.04.006] |
|
Effect of pH and salts on microstructure and viscoelastic pr...
2018-04-03 [10.1016/j.foodhyd.2018.04.005] |
|
Incidence of milling energy on dry-milling attributes of ric...
2018-04-03 [10.1016/j.foodhyd.2018.03.051] |
|
Stabilization of oil continuous emulsions with colloidal par...
2018-04-03 [10.1016/j.foodhyd.2018.04.004] |