Investigation of the Water Adsorption Properties and Structural Stability of MIL-100(Fe) with Different Anions
Yen-Ru Chen, Kai-Hsin Liou, Dun-Yen Kang, Jiun-Jen Chen, Li-Chiang Lin
文献索引:10.1021/acs.langmuir.7b04399
全文:HTML全文
摘要
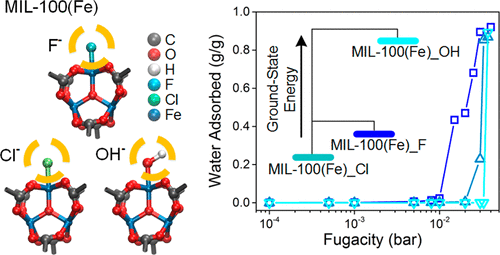
Investigating metal–organic frameworks (MOFs) as water adsorbents has drawn increasing attention for their potential in energy-related applications such as water production and heat transformation. A specific MOF, MIL-100(Fe), is of particular interest for its large adsorption capacity with the occurrence of water condensation at a relatively low partial pressure. In the synthesis of MIL-100(Fe), depending on the reactants, structures with varying anion terminals (e.g., F–, Cl–, or OH–) on the metal trimer have been reported. In this study, we employed molecular simulations and density functional theory calculations for investigating the water adsorption behaviors and the relative structural stability of MIL-100(Fe) with different anions. We also proposed a possible defective structure and explored its water adsorption properties. The results of this study are in good agreement with the experimental measurements and are in support of the observations reported in the literature. Understanding the spatial configurations and energetics of water molecules in these materials has also shed light on their adsorption mechanism at the atomic level.
|
Floating and Tether-Coupled Adhesion of Bacteria to Hydropho...
2018-04-18 [10.1021/acs.langmuir.7b04331] |
|
A Concentration-Dependent Insulin Immobilization Behavior of...
2018-04-18 [10.1021/acs.langmuir.8b00377] |
|
Numerical Study of Surfactant Dynamics during Emulsification...
2018-04-18 [10.1021/acs.langmuir.8b00123] |
|
Bifunctionality of Iminodiacetic Acid-Modified Lysozyme on I...
2018-04-17 [10.1021/acs.langmuir.8b00254] |
|
Maximum Spreading and Rebound of a Droplet Impacting onto a ...
2018-04-17 [10.1021/acs.langmuir.8b00625] |