Combined quantitative FTIR and online GC study of Fischer-Tropsch synthesis involving co-fed ethylene
Andrew I. McNab, Alan J. McCue, Davide Dionisi, James A. Anderson
文献索引:10.1016/j.jcat.2018.03.026
全文:HTML全文
摘要
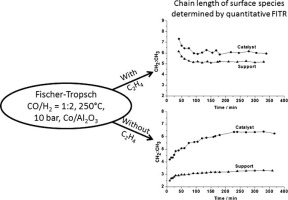
Combined quantitative in-situ FTIR and online gas chromatography have been applied to assess the effect of co-feeding ethylene on the length and nature of the hydrocarbon species formed on cobalt catalysts and the detected reaction products during Fischer-Tropsch synthesis. Reaction data showed that co-feeding ethylene leads to a decrease in methane selectivity and an increase in selectivity to C5-6 products. Comparison of the average length of the adsorbed species during reactions, in the presence and absence of co-fed ethylene reveals that ethylene may be incorporated into species which re-adsorb to the γ-alumina support from the gas phase. Additionally, co-feeding of ethylene appears to diminish the extent to which hydrocarbon species are transferred via spillover to the support. Varying the reaction temperature resulted in changes to both the average lengths of the adsorbed species and those of the reaction products. However, no direct relationship between surface species and reaction products could be determined, possibly due to the lack of detectable oxygenates in the product stream.
|
Ethylene versus ethane: A DFT-based selectivity descriptor f...
2018-04-06 [10.1016/j.jcat.2018.03.019] |
|
Mechanistic insight into cobalt-catalyzed stereodivergent se...
2018-04-06 [10.1016/j.jcat.2018.03.016] |
|
Principles determining the activity of magnetic oxides for e...
2018-03-30 [10.1016/j.jcat.2018.03.012] |
|
Synthesis and characterization of Ag@Carbon core-shell spher...
2018-03-30 [10.1016/j.jcat.2018.02.029] |
|
Mechanistic investigations into the cyclopropanation of elec...
2018-03-30 [10.1016/j.jcat.2018.02.013] |