Mechanism and kinetics of photochemical transformation of ketoprofen and its degradation intermediates
Lenka Hykrdová, Oliver Bajt, Jaromír Jirkovský
文献索引:10.1016/j.jhazmat.2018.03.048
全文:HTML全文
摘要
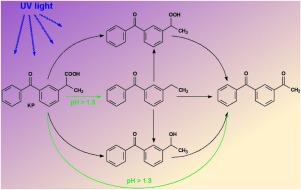
Ketoprofen, 2-(3-benzoylphenyl)-propionic acid, a widely used non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug, is considered as an important water pollutant. Kinetics and mechanism of its photolytic transformation in aqueous solutions was studied experimentally and partial reaction steps were modelled by means of quantum chemistry methods. While the rate of ketoprofen photolysis was not significantly affected by its acid-base equilibrium, a marked influence of pH on the subsequent degradation reactions was observed. At pH 1.3, two oxygenated primary products were identified, that underwent fast photolysis. Deprotonated form of ketoprofen was transformed preferentially to ethylbenzophenone and further degradation proceeded substantially slower. Oxygen participated on photolytic processes both as a reactant and the triplet state quencher. The active involvement of water molecules in the reaction mechanism was investigated by comparative experiments in acetonitrile. The phototransformation mechanism proposed based on the experimental data corresponded well with the theoretical results.
|
Humic acid attenuation of silver nanoparticle toxicity by io...
2018-04-11 [10.1016/j.jhazmat.2018.04.019] |
|
In Situ Preparation of Highly Stable Polyaniline/W18O49 Hybr...
2018-04-10 [10.1016/j.jhazmat.2018.04.005] |
|
Effects of Trifluralin on the Soil Microbial Community and Fu...
2018-04-10 [10.1016/j.jhazmat.2018.04.012] |
|
Effects of different oxyanions in solution on the precipitat...
2018-04-09 [10.1016/j.jhazmat.2018.04.016] |
|
Comparison of constant, pulsed, incremental and decremental ...
2018-04-08 [10.1016/j.jhazmat.2018.04.002] |