| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|
 |
甘油
CAS:56-81-5 |
|
 |
白藜芦醇
CAS:501-36-0 |
|
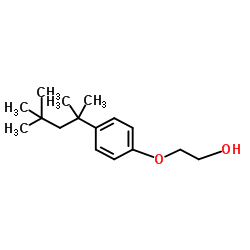 |
4-叔辛基苯酚单氧化物
CAS:2315-67-5 |
|
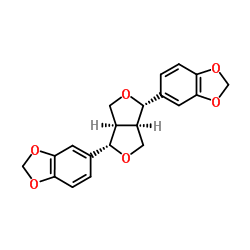 |
芝麻素
CAS:607-80-7 |
|
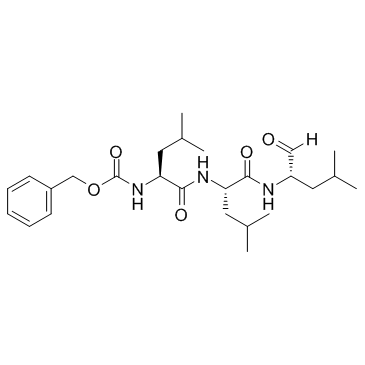 |
蛋白酶体抑制剂
CAS:133407-82-6 |