| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|
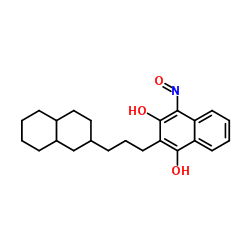 |
酯酶 来源于猪肝脏
CAS:9016-18-6 |
|
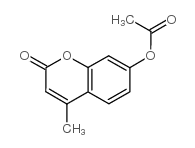 |
7-乙酰氧基-4-甲基香豆素
CAS:2747-05-9 |