| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|
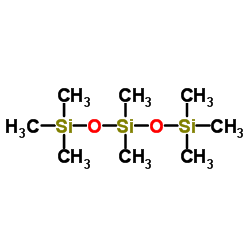 |
八甲基三硅氧烷
CAS:107-51-7 |
|
 |
六甲基二硅氧烷
CAS:107-46-0 |
|
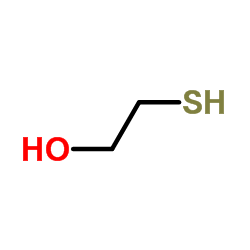 |
巯基乙醇
CAS:60-24-2 |
|
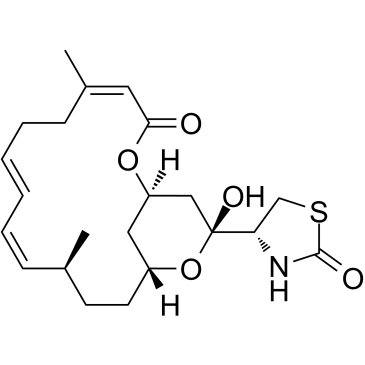 |
红海海绵素 A
CAS:76343-93-6 |
|
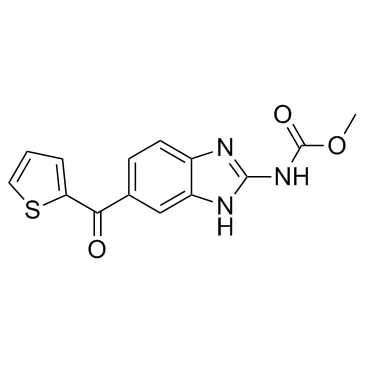 |
诺考达唑
CAS:31430-18-9 |