Influence of polyelectrolyte on the thermosensitive property of PNIPAAm-based copolymer hydrogels.
Xian-Zheng Zhang, Chih-Chang Chu
文献索引:J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 18(9) , 1771-9, (2007)
全文:HTML全文
摘要
A new family of poly(NIPAAm-co-2-acrylamido-2-methyl-1-propanesulfonic acid) [P(NIPAAm-co-AMPSA)] hydrogels was synthesized by incorporating negative charged AMPSA to the backbone of the PNIPAAm-based hydrogel. The effect of polyelectrolyte (i.e., PAMPSA) on the thermosensitive property of PNIPAAm hydrogels was investigated. It was found that P(NIPAAm-co-AMPSA) hydrogels exhibited unique honey-comb-like 3D porous structure having rigid cell wall as well as enhanced mechanical property. The incorporation of AMPSA into PNIPAAm backbones also led to a significant increase in swelling capability at room temperature when comparing to pure PNIPAAm hydrogels. In addition, the shrinking rate upon heating was significantly improved if the AMPSA content in P(NIPAAm-co-AMPSA) hydrogels was less than 10 wt%.
相关化合物
| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 分子式 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|---|
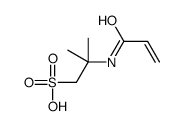 |
聚(2-丙烯酰胺-2-甲基-1-丙磺酸)
CAS:27119-07-9 |
C7H13NO4S |
|
PAA-PAMPS copolymers as an efficient tool to control CaCO3 s...
2013-03-05 [Langmuir 29(9) , 3080-8, (2013)] |
|
Dielectric properties of micellar aggregates due to the self...
2011-03-17 [J. Phys. Chem. B 115(10) , 2196-204, (2011)] |
|
Anti-angiogenic activity of heparin-like polysulfonated poly...
2010-11-01 [Biomaterials 31(31) , 7863-72, (2010)] |
|
Hyaluronic acid affects the in vitro induction effects of sy...
2013-01-01 [BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 14 , 56, (2013)] |
|
Surface sliding friction of negatively charged polyelectroly...
2007-04-15 [Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 56(1-2) , 296-302, (2007)] |