| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|
 |
氢氧化钠
CAS:1310-73-2 |
|
 |
3-乙基-2,4-戊烷二酮
CAS:1540-34-7 |
|
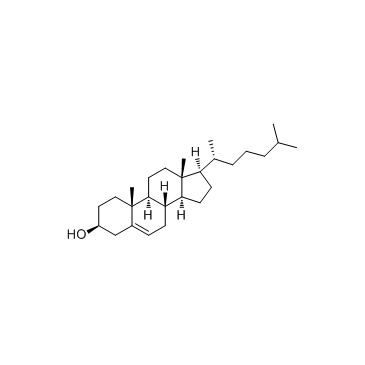 |
胆固醇
CAS:57-88-5 |
|
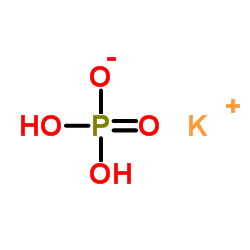 |
磷酸二氢钾
CAS:7778-77-0 |
|
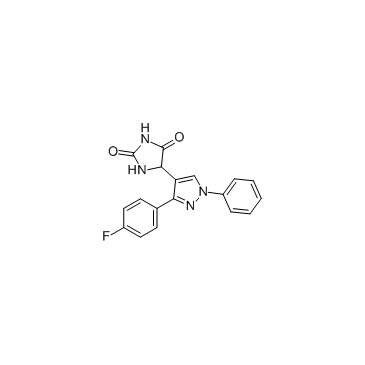 |
5-(3-(4-氟苯基)-1-苯基-1H-吡唑-4-基)咪唑啉-2,4-二酮
CAS:484049-04-9 |