GTP hydrolysis is essential for protein import into the mitochondrial matrix.
N B Sepuri, N Schülke, D Pain
文献索引:J. Biol. Chem. 273(3) , 1420-4, (1998)
全文:HTML全文
摘要
Protein import into the innermost compartment of mitochondria (the matrix) requires a membrane potential (delta psi) across the inner membrane, as well as ATP-dependent interactions with chaperones in the matrix and cytosol. The role of nucleoside triphosphates other than ATP during import into the matrix, however, remains to be determined. Import of urea-denatured precursors does not require cytosolic chaperones. We have therefore used a purified and urea-denatured preprotein in our import assays to bypass the requirement of external ATP. Using this modified system, we demonstrate that GTP stimulates protein import into the matrix; the stimulatory effect is directly mediated by GTP hydrolysis and does not result from conversion of GTP to ATP. Both external GTP and matrix ATP are necessary; neither one can substitute for the other if efficient import is to be achieved. These results suggest a "push-pull" mechanism of import, which may be common to other post-translational translocation pathways.
相关化合物
| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 分子式 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|---|
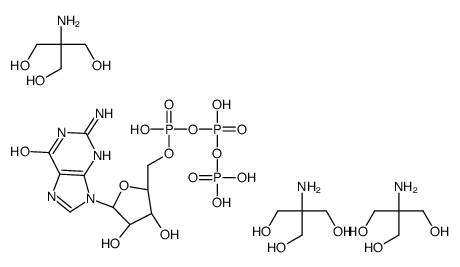 |
鸟苷 5′-三磷酸盐 三羟甲基氨基甲烷盐
CAS:103192-46-7 |
C22H49N8O23P3 |
|
The role of guanosine 5'-triphosphate in polypeptide chain e...
1978-09-21 [Biochim. Biophys. Acta 505(1) , 95-127, (1978)] |
|
Phosphoinositides, inositol phosphates, and phospholipase C ...
2006-01-01 [Methods Mol. Biol. 329 , 127-49, (2006)] |
|
Structural and functional model for ionic (K(+)/Na(+)) and p...
2009-07-03 [J. Mol. Biol. 390(1) , 17-25, (2009)] |
|
Galanin-binding sites in the female rat brain are regulated ...
1995-06-01 [Neuroendocrinology 61(6) , 646-54, (1995)] |
|
Microtubule elongation and guanosine 5'-triphosphate hydroly...
1987-07-14 [Biochemistry 26(14) , 4428-37, (1987)] |