| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|
 |
氯化钠
CAS:7647-14-5 |
|
 |
十二烷基硫酸钠
CAS:151-21-3 |
|
 |
L-半胱氨酸
CAS:52-90-4 |
|
 |
1,1'-双十八烷基-3,3,3',3'-四甲基吲哚菁高氯酸盐
CAS:41085-99-8 |
|
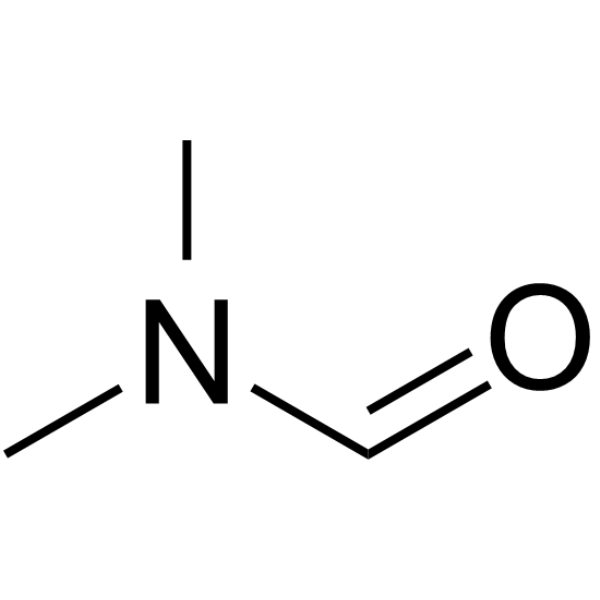 |
N,N-二甲基甲酰胺
CAS:68-12-2 |
|
 |
氯化钠-35cl
CAS:20510-55-8 |
|
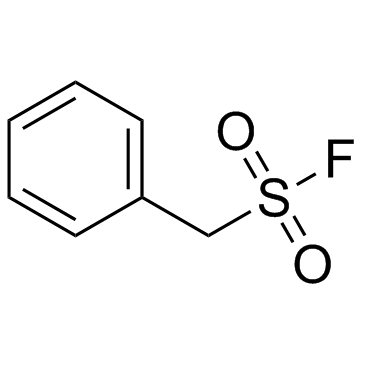 |
苄磺酰氟
CAS:329-98-6 |
|
![4-[[(4S,5R)-4,5-双(4-氯苯基)-4,5-二氢-2-[4-甲氧基-2-(1-甲基乙氧基)苯基]-1H-咪唑-1-YL]羰基]-2-哌嗪酮 结构式](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/103/675576-98-4.png) |
4-[[(4S,5R)-4,5-双(4-氯苯基)-4,5-二氢-2-[4-甲氧基-2-(1-甲基乙氧基)苯基]-1H-咪唑-1-YL]羰基]-2-哌嗪酮
CAS:675576-98-4 |
|
 |
乙二胺四乙酸
CAS:60-00-4 |