| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|
 |
氯化钠
CAS:7647-14-5 |
|
 |
佛司可林
CAS:66575-29-9 |
|
 |
无水氯化钙
CAS:10043-52-4 |
|
 |
4-羟乙基哌嗪乙磺酸
CAS:7365-45-9 |
|
 |
氯化钠-35cl
CAS:20510-55-8 |
|
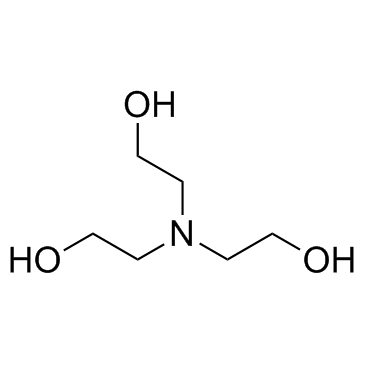 |
三乙醇胺
CAS:102-71-6 |
|
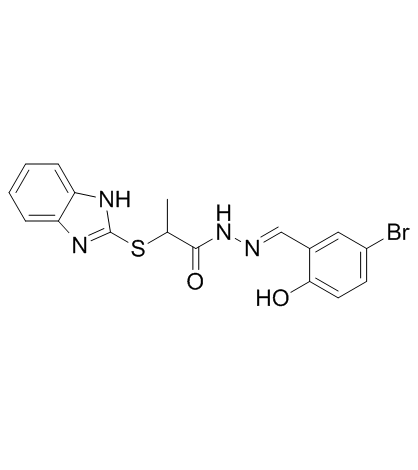 |
KH7
CAS:330676-02-3 |
|
![2,4,6-三甲基-N-[3-(三氟甲基)苯基]苯磺酰胺 结构式](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/404/200933-14-8.png) |
2,4,6-三甲基-N-[3-(三氟甲基)苯基]苯磺酰胺
CAS:200933-14-8 |
|
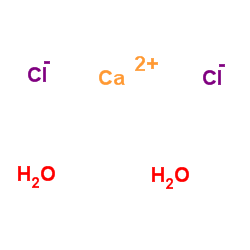 |
二水氯化钙
CAS:10035-04-8 |
|
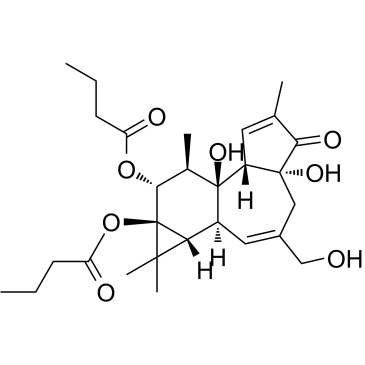 |
佛波醇 12,13-二丁酸酯
CAS:37558-16-0 |