| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|
 |
乙醇
CAS:64-17-5 |
|
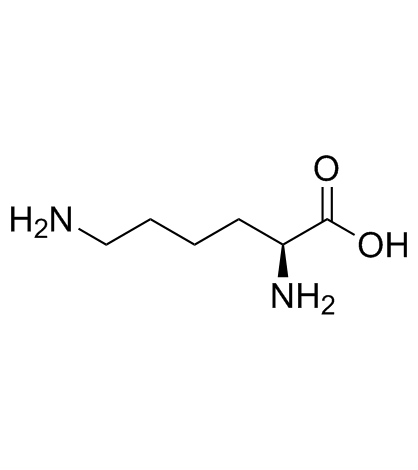 |
L-赖氨酸
CAS:56-87-1 |
|
 |
L-赖氨酸盐酸盐
CAS:657-27-2 |
|
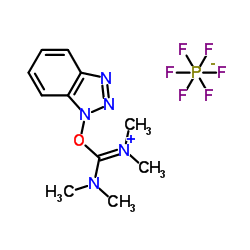 |
苯并三氮唑-N,N,N',N'-四甲基脲六氟磷酸酯
CAS:94790-37-1 |
|
 |
抗菌肽A
CAS:80451-04-3 |
|
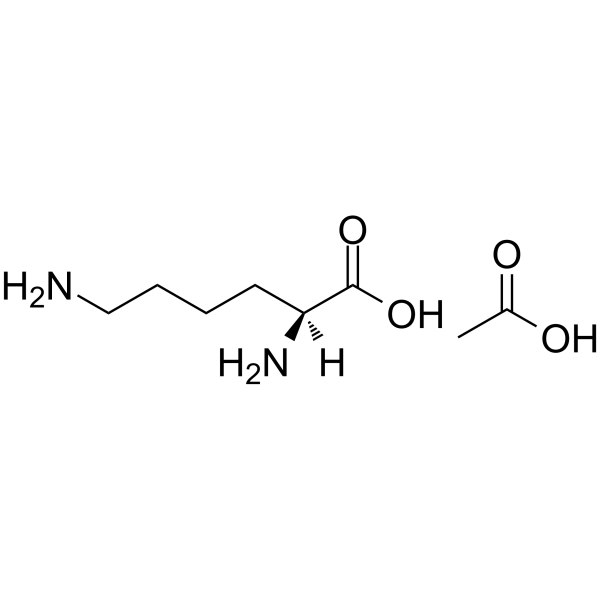 |
醋酸赖氨酸
CAS:57282-49-2 |