| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|
 |
乙醇
CAS:64-17-5 |
|
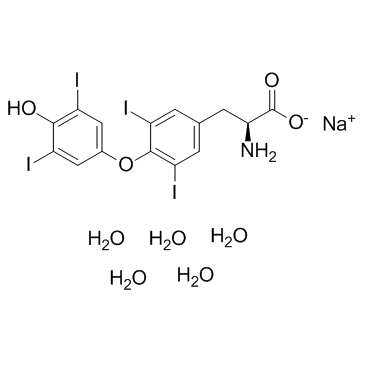 |
L-甲状腺素钠五水合物(左甲状腺素钠)
CAS:6106-07-6 |
|
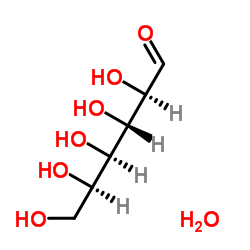 |
葡萄糖,一水
CAS:14431-43-7 |