Development of a substrate-coupled biocatalytic process driven by an NADPH-dependent sorbose reductase from Candida albicans for the asymmetric reduction of ethyl 4-chloro-3-oxobutanoate.
Ping Cai, Mingdong An, Lin Xu, Sheng Xu, Ning Hao, Yan Li, Kai Guo, Ming Yan
文献索引:Biotechnol. Lett. 34(12) , 2223-7, (2012)
全文:HTML全文
摘要
A substrate-coupled biocatalytic process was developed based on the reactions catalyzed by an NADPH-dependent sorbose reductase (SOU1) from Candida albicans in which ethyl 4-chloro-3-oxobutanoate (COBE) was reduced to (S)-4-chloro-3-hydroxybutanoate [(S)-CHBE], while NADPH was regenerated by the same enzyme via oxidation of sugar alcohols. (S)-CHBE yields of 1,140, 1,150, and 780 mM were obtained from 1,220 mM COBE when sorbitol, mannitol, and xylitol were used as co-substrates, respectively. Optimization of COBE and sorbitol proportions resulted in a maximum yield of (S)-CHBE (2,340 mM) from 2,500 mM COBE, and the enantiomeric excess was 99.6 %. The substrate-coupled system driven by SOU1 maintained a stable pH and a robust intracellular NADPH circulation; thus, pH adjustment and addition of extra coenzymes were unnecessary.
相关化合物
| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 分子式 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|---|
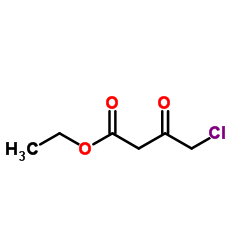 |
4-氯乙酰乙酸乙酯
CAS:638-07-3 |
C6H9ClO3 |
|
Construction of a two-strain system for asymmetric reduction...
2006-03-01 [Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 70(1) , 40-6, (2006)] |
|
Purification and characterization of an alpha-haloketone-res...
2003-10-01 [Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 67(10) , 2145-53, (2003)] |
|
A novel carbonyl reductase from Pichia stipitis for the prod...
2009-04-01 [Biotechnol. Lett. 31(4) , 537-42, (2009)] |
|
Biosimulation of drug metabolism—A yeast based model
2009-01-01 [Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 36(1) , 157-70, (2009)] |
|
Enantioselective bioconversion using Escherichia coli cells ...
2010-09-01 [J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 20(9) , 1300-6, (2010)] |