| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|
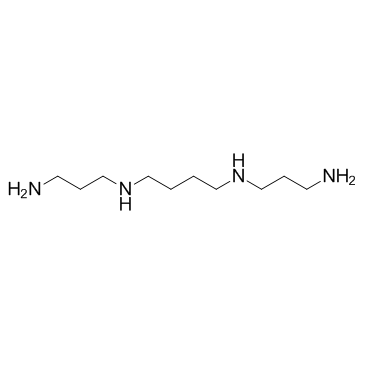 |
精胺
CAS:71-44-3 |
|
 |
N1,n4-二(buta-2,3-二enyl)丁烷-1,4-二胺双盐酸盐
CAS:93565-01-6 |