Involvement of poly(ADP-ribose) synthetase in acoustic trauma of the cochlea.
Keiji Tabuchi, Tomohumi Hoshino, Hidekazu Murashita, Keiko Oikawa, Isao Uemaetomari, Bungo Nishimura, Tadamichi Tobita, Akira Hara
文献索引:Tohoku J. Exp. Med. 200(4) , 195-202, (2003)
全文:HTML全文
摘要
We investigated effects of poly(ADP-ribose) synthetase (PARS) inhibitors on acoustic trauma. Albino guinea pigs were intravenously given 3-aminobenzamide, nicotinamide or 3-aminobenzoic acid (an inactive analog of 3-aminobenzamide) just prior to exposure to a 2 kHz pure tone of 120 dB sound pressure level (SPL) for 10 minutes. The threshold of the compound action potential (CAP) and the amplitude of distortion-product otoacoustic emissions (DPOAEs) were measured before and 4 hours after the acoustic overexposure. Statistically significant decreases in the CAP threshold shifts and significant increases in the DPOAE amplitudes were observed 4 hours after the acoustic overexposure in the animals treated with 3-aminobenzamide or nicotinamide, whereas 3-aminobenzoic acid did not exert any protective effect. These results strongly suggest that excessive activation of PARS is involved in generation of the acoustic trauma.
相关化合物
| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 分子式 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|---|
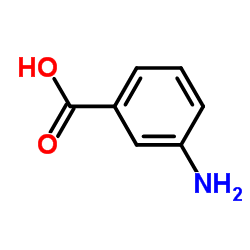 |
间氨基苯甲酸
CAS:99-05-8 |
C7H7NO2 |
|
One-pot enzymatic conversion of carbon dioxide and utilizati...
2015-04-07 [Environ. Sci. Technol. 49(7) , 4466-72, (2015)] |
|
Synthesis and evaluation of novel aromatic substrates and co...
2008-05-15 [Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 18 , 3122-5, (2008)] |
|
Selective Gating of Neuronal Activity by Intrinsic Propertie...
2015-07-08 [J. Neurosci. 35 , 9799-810, (2015)] |
|
Differential 12C-/13C-isotope dansylation labeling and fast ...
2009-05-15 [Anal. Chem. 81(10) , 3919-32, (2009)] |
|
Three-dimensional quantitative structure-activity relationsh...
2011-11-01 [Bioorg. Med. Chem. 19 , 6409-18, (2011)] |