| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|
 |
甘油
CAS:56-81-5 |
|
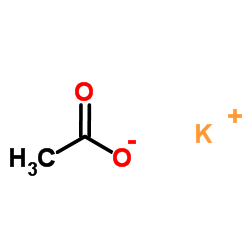 |
醋酸钾
CAS:127-08-2 |
|
 |
冰醋酸
CAS:64-19-7 |
|
 |
辅酶I
CAS:53-84-9 |
|
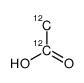 |
乙酸-12C2
CAS:1173022-32-6 |
|
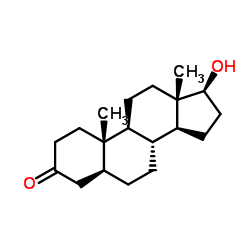 |
雄诺龙
CAS:521-18-6 |
|
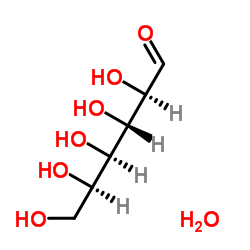 |
葡萄糖,一水
CAS:14431-43-7 |
|
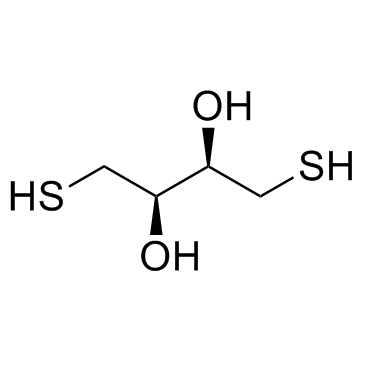 |
DL-二硫苏糖醇
CAS:3483-12-3 |
|
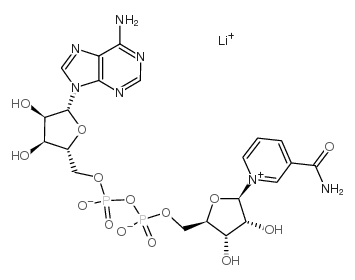 |
Β-菸鹼醯胺腺嘌呤二核苷酸
CAS:64417-72-7 |