| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|
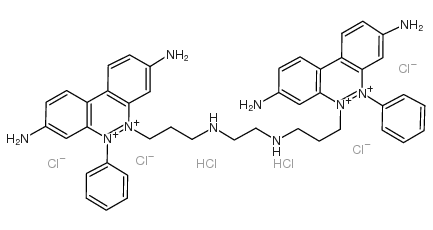 |
同二聚乙胺
CAS:61926-22-5 |
|
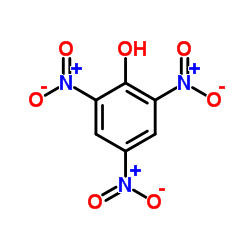 |
苦味酸
CAS:88-89-1 |
|
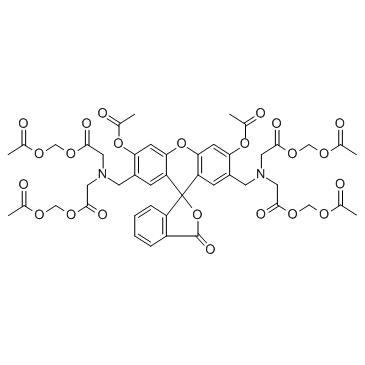 |
细胞染色剂黄绿素-AM
CAS:148504-34-1 |
|
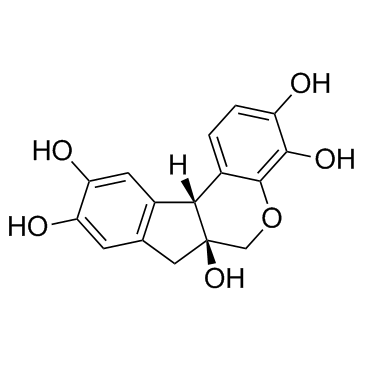 |
苏木精
CAS:517-28-2 |
|
 |
N-乙烯基吡咯烷酮
CAS:88-12-0 |
|
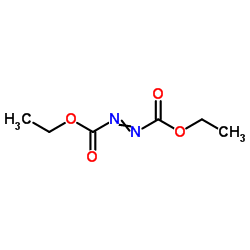 |
偶氮二甲酸二乙酯
CAS:1972-28-7 |
|
 |
2,2-二甲氧基-2-苯基苯乙酮
CAS:24650-42-8 |