Cleavages of the O- and C-glucosyl bonds of anthrone and 10,10'-bianthrone derivatives by human intestinal bacteria.
M Hattori, T Akao, K Kobashi, T Namba
文献索引:Pharmacology 47 Suppl 1 , 125-33, (1993)
全文:HTML全文
摘要
A strictly anaerobic bacterium, Bifidobacterium sp. SEN, capable of hydrolyzing the O-glucosyl of sennosides was isolated from human feces. The bacterium stepwisely hydrolyzed sennoside B to sennidin B through sennidin-8-monoglucoside in PYF medium but not in GAM broth. Addition of D-glucose to PYF medium resulted in loss of the hydrolyzing activity in culture but addition of D-fructose did not affect the activity. Coculture of this bacterium with Peptostreptococcus intermedius led to rapid accumulation of rhein anthrone in the medium. Similarly, a bacterium, Eubacterium sp. BAR, capable of cleaving the C-glucosyl of barbaloin was isolated from human feces. This bacterium grew in PYF medium containing barbaloin and produced enzyme(s) that cleave(s) the C-glucosyl. The induction of the enzymes was completely inhibited in the presence of D-glucose. Nojirimycin inhibited the enzyme activity induced by barbaloin but it did not inhibit the bacterial growth in the presence of D-glucose.
相关化合物
| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 分子式 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|---|
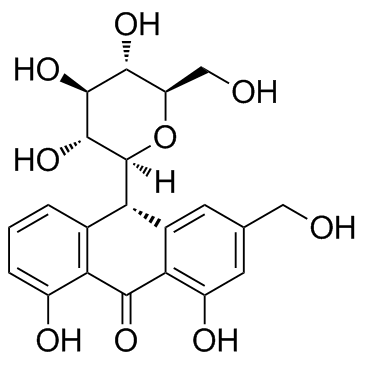 |
芦荟苷
CAS:1415-73-2 |
C21H22O9 |
|
The content of secondary phenol metabolites in pruned leaves...
2008-10-01 [J. Nat. Med. 62(4) , 430-5, (2008)] |
|
Determination of aloenin, barbaloin and isobarbaloin in aloe...
2001-03-05 [J. Chromatogr. B. Biomed. Sci. Appl. 752(1) , 91-7, (2001)] |
|
Liquid chromatographic determination of barbaloin (aloin) in...
1985-01-01 [J. Assoc. Off. Anal. Chem. 68(3) , 493-4, (1985)] |
|
Isolation of a human intestinal bacterium capable of transfo...
1991-02-01 [Planta Med. 57(1) , 15-9, (1991)] |
|
Metabolism of barbaloin by intestinal bacteria.
1988-11-01 [Chem. Pharm. Bull. 36(11) , 4462-6, (1988)] |