The branched-chain dodecylbenzene sulfonate degradation pathway of Pseudomonas aeruginosa W51D involves a novel route for degradation of the surfactant lateral alkyl chain.
J Campos-García, A Esteve, R Vázquez-Duhalt, J L Ramos, G Soberón-Chávez
文献索引:Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 65(8) , 3730-4, (1999)
全文:HTML全文
摘要
Pseudomonas aeruginosa W51D is able to grow by using branched-chain dodecylbenzene sulfonates (B-DBS) or the terpenic alcohol citronellol as a sole source of carbon. A mutant derived from this strain (W51M1) is unable to degrade citronellol but still grows on B-DBS, showing that the citronellol degradation route is not the main pathway involved in the degradation of the surfactant alkyl moiety. The structures of the main B-DBS isomers and of some intermediates were identified by gas chromatography-mass spectrometric analysis, and a possible catabolic route is proposed.
相关化合物
| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 分子式 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|---|
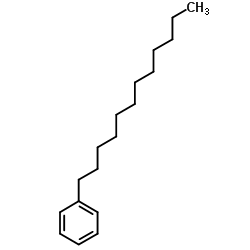 |
正十二烷基苯
CAS:123-01-3 |
C18H30 |
|
Broad spectrum analysis of polar and apolar organic compound...
2015-07-24 [J. Chromatogr. A. 1404 , 28-38, (2015)] |
|
In situsynthesis of di-n-butyll-tartrate–boric acid complex ...
2009-01-01 [J. Chromatogr. A. 1216(45) , 7932-40, (2009)] |
|
The degradation of 1-phenylalkanes by an oil-degrading strai...
1985-01-01 [Antonie van Leeuwenhoek 51(1) , 45-56, (1985)] |
|
Validation of an assay for the determination of levoglucosan...
2014-09-01 [Anal. Bioanal. Chem 406(22) , 5283-92, (2014)] |
|
Design and characterization of antimicrobial usnic acid load...
2015-01-01 [Mater. Sci. Eng. C. Mater. Biol. Appl. 52 , 72-81, (2015)] |