| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|
 |
1,2-二羟基蒽醌,茜素
CAS:72-48-0 |
|
 |
抗坏血酸
CAS:50-81-7 |
|
 |
甲醛
CAS:50-00-0 |
|
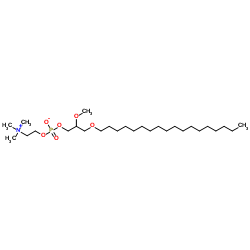 |
依地芬
CAS:70641-51-9 |
|
 |
4',6-二脒基-2-苯基吲哚二盐酸盐
CAS:28718-90-3 |
|
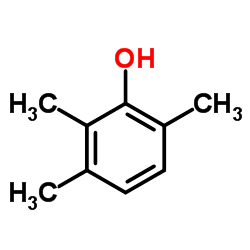 |
2,3,6-三甲基苯酚
CAS:2416-94-6 |