| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|
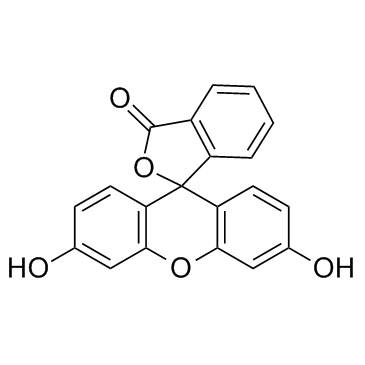 |
荧光素
CAS:2321-07-5 |
|
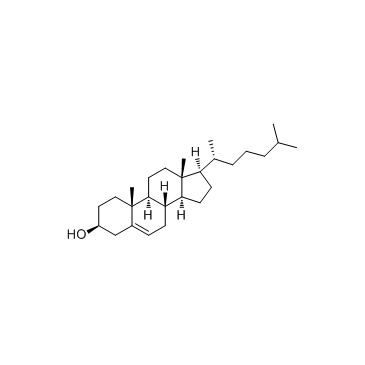 |
胆固醇
CAS:57-88-5 |
|
 |
L-谷氨酰胺
CAS:56-85-9 |
|
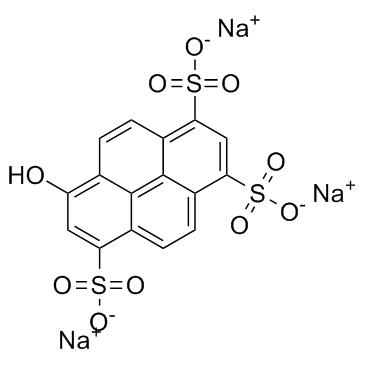 |
8-羟基-1,3,6-芘三磺酸三钠
CAS:6358-69-6 |
|
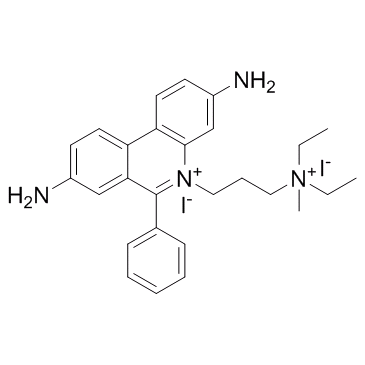 |
碘化丙啶
CAS:25535-16-4 |