| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|
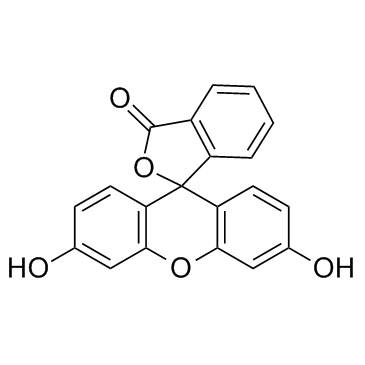 |
荧光素
CAS:2321-07-5 |
|
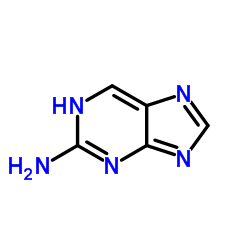 |
2-氨基嘌呤
CAS:452-06-2 |
|
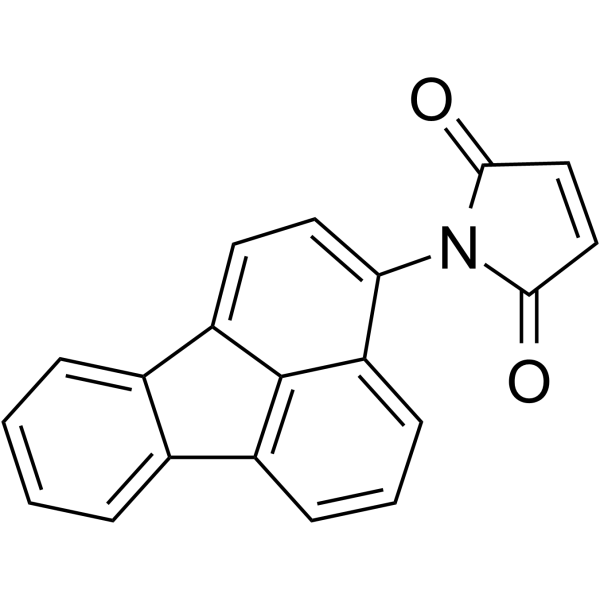 |
N-(3-Fluoranthyl)顺丁烯二酰亚胺
CAS:60354-76-9 |