| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|
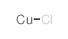 |
氯化亚铜
CAS:7758-89-6 |
|
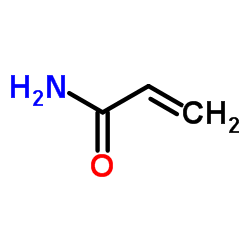 |
丙烯酰胺
CAS:79-06-1 |
|
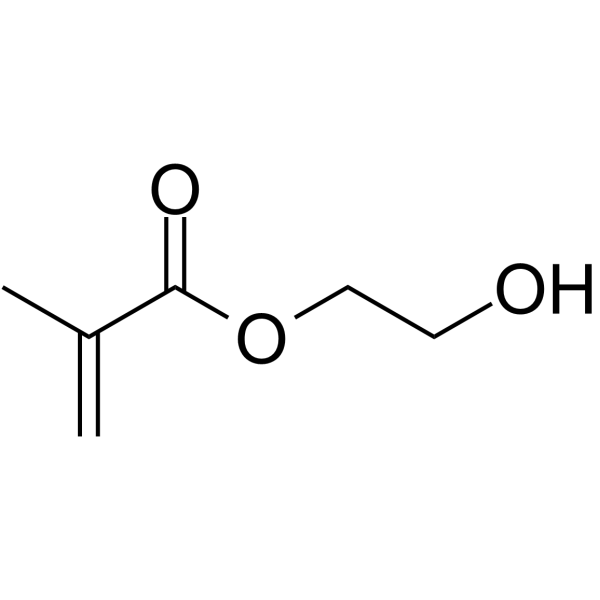 |
甲基丙烯酸羟乙酯
CAS:868-77-9 |
|
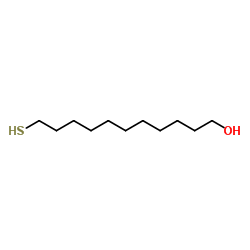 |
11-巯基-1-十一醇
CAS:73768-94-2 |
|
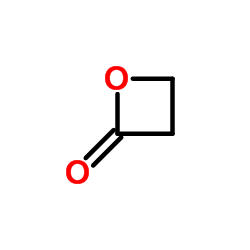 |
丙内酯
CAS:57-57-8 |