| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|
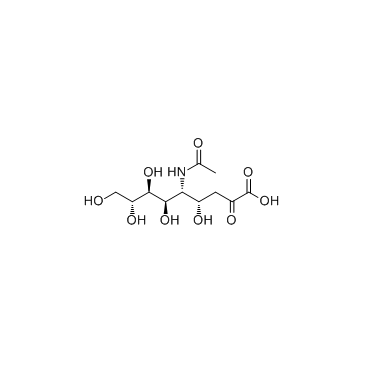 |
N-乙酰神经氨酸
CAS:131-48-6 |
|
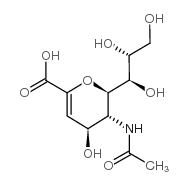 |
N-乙酰-2,3-二脱氢-2-脱氧神经氨酸
CAS:24967-27-9 |