| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|
 |
2-甲基-D-苯丙氨酸
CAS:17350-84-4 |
|
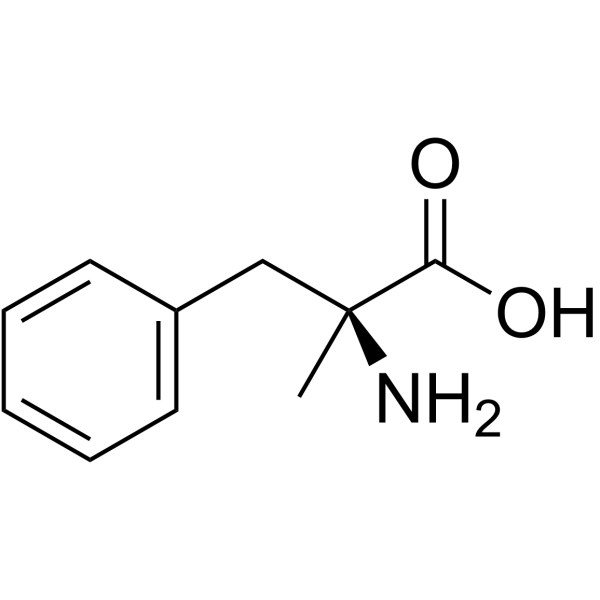 |
a-甲基-L-苯丙氨酸
CAS:23239-35-2 |
|
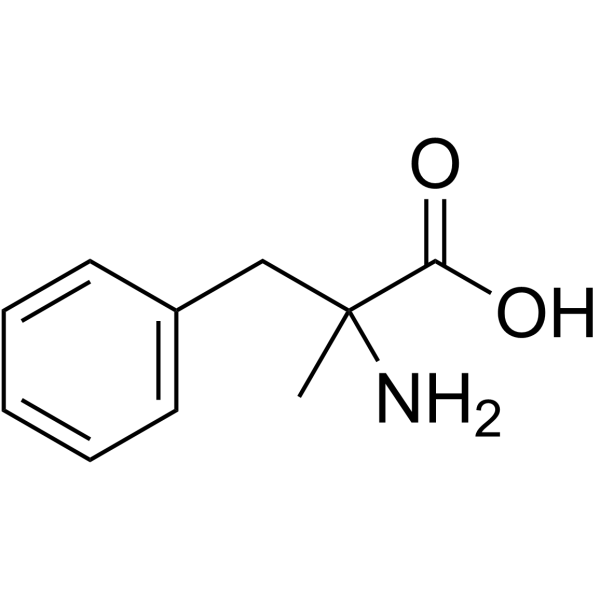 |
α-甲基-DL-苯丙氨酸
CAS:1132-26-9 |