| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|
 |
D(+)-无水葡萄糖
CAS:50-99-7 |
|
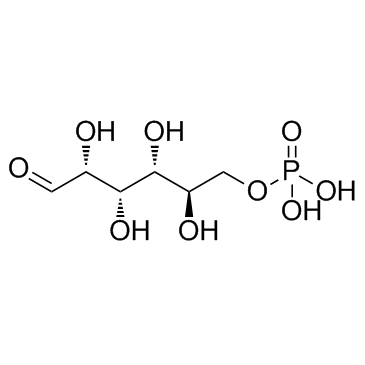 |
D-葡糖-6-磷酸
CAS:56-73-5 |
|
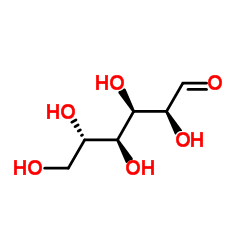 |
L-(-)-无水葡萄糖
CAS:921-60-8 |
|
 |
D-果糖-1,6-二磷酸二钙盐
CAS:6055-82-9 |