| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|
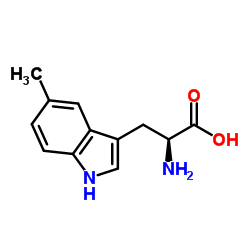 |
5-甲基-DL-色氨酸
CAS:951-55-3 |
|
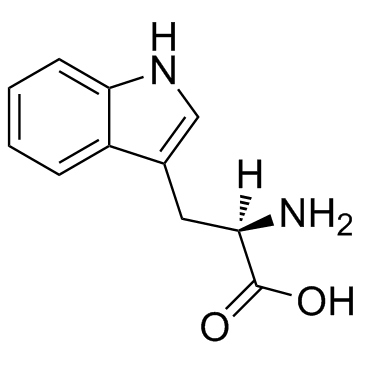 |
D-色氨酸
CAS:153-94-6 |
|
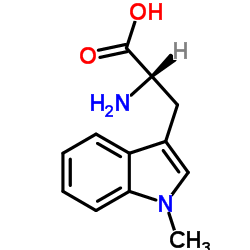 |
相思子碱
CAS:21339-55-9 |
|
 |
DL-5-甲氧基色氨酸
CAS:28052-84-8 |