Mechanism underlying hypokalemia induced by trimethyltin chloride: Inhibition of H+/K+-ATPase in renal intercalated cells
Xiaojiang Tang, Xiaojun Yang, Guanchao Lai, Jinhui Guo, Lihua Xia, Banghua Wu, Yuxuan Xie, Ming Huang, Jiabin Chen, Xiaolin Ruan, Gang Sui, Yichen Ge, Wulin Zuo, Na Zhao, Guanghua Zhu, Jinxin Zhang, Laiyu Li, Wenliang Zhou, Xiaojiang Tang, Xiaojun Yang, Guanchao Lai, Jinhui Guo, Lihua Xia, Banghua Wu, Yuxuan Xie, Ming Huang, Jiabin Chen, Xiaolin Ruan, Gang Sui, Yichen Ge, Wulin Zuo, Na Zhao, Guanghua Zhu, Jinxin Zhang, Laiyu Li, Wenliang Zhou, Xiaojiang Tang, Xiaojun Yang, Guanchao Lai, Jinhui Guo, Lihua Xia, Banghua Wu, Yuxuan Xie, Ming Huang, Jiabin Chen, Xiaolin Ruan, Gang Sui, Yichen Ge, Wulin Zuo, Na Zhao, Guanghua Zhu, Jinxin Zhang, Laiyu Li, Wenliang Zhou
文献索引:Toxicology 271(1-2) , 45-50, (2010)
全文:HTML全文
摘要
Trimethyltin chloride (TMT), a byproduct of plastic stabilizers, has caused 67 poisoning accidents in the world; more than 98% (1814/1849) of the affected patients since 1998 have been in China. As a long-established toxic chemical, TMT severely affects the limbic system and the cerebellum; however, its relationship with hypokalemia, a condition observed in the majority of the cases in the last decade, remains elusive. To understand the mechanism underlying hypokalemia induced by TMT, Sprague–Dawley (SD) rats were administered TMT to determine the relationship between H +/K +-ATPase activity and the blood and urine K + concentration and pH, respectively. H +/K +-ATPase protein and mRNA were observed too. In vitro changes to intracellular pH, K + channels in renal cells were measured. The results showed that TMT increased potassium leakage from the kidney, raised urine pH, and inhibited H +/K +-ATPase activity both in vitro and in vivo. In the tested animals, H +/K +-ATPase activity was positively correlated with the decrease of plasma K + and blood pH but was negatively correlated with the increase of urine K + and urine pH ( P < 0.01), while TMT did not change the expression of H +/K +-ATPase protein and mRNA. TMT decreased intracellular pH and opened K + channels in renal intercalated cells. Our findings suggest TMT can directly inhibit the activity of H +/K +-ATPases in renal intercalated cells, reducing urine K + reabsorption and inducing hypokalemia.
相关化合物
| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 分子式 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|---|
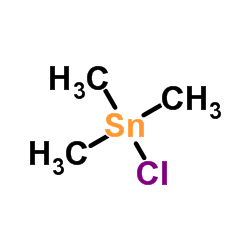 |
三甲基氯化锡
CAS:1066-45-1 |
C3H9ClSn |
|
Adsorption and degradation processes of tributyltin and trim...
2015-10-01 [Environ. Res. 142 , 511-21, (2015)] |
|
Synthesis, characterization and biocidal activity of new org...
2010-03-01 [Eur. J. Med. Chem. 45 , 883-9, (2010)] |
|
Trimethyltin-Induced Microglial Activation via NADPH Oxidase...
2015-01-01 [Mediators Inflamm. 2015 , 729509, (2015)] |
|
The selective norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor atomoxetine ...
2012-05-15 [Eur. J. Pharmacol. 683(1-3) , 148-54, (2012)] |
|
Blockade of glutamatergic and GABAergic receptor channels by...
2005-01-01 [Br. J. Pharmacol. 144(2) , 283-92, (2005)] |