| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|
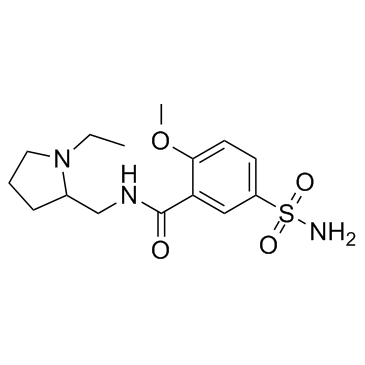 |
舒必利
CAS:15676-16-1 |
|
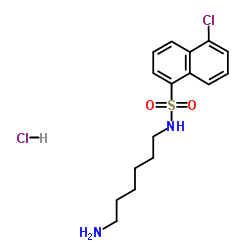 |
N-(6-氨基己基)-5-氯-1-萘磺酰胺盐酸盐
CAS:61714-27-0 |
|
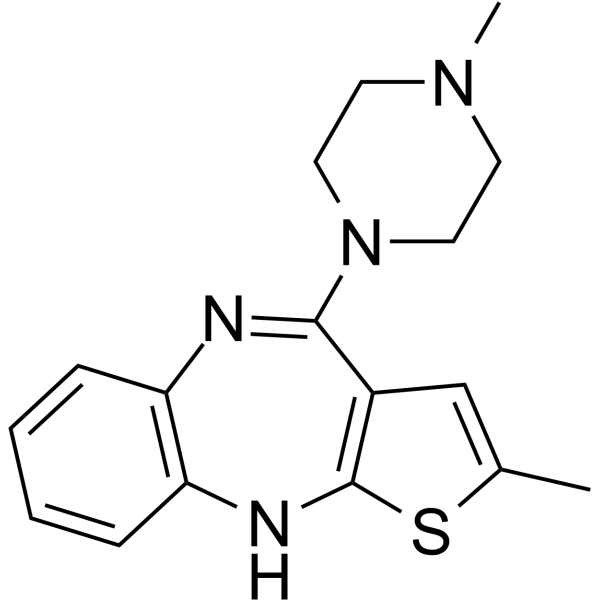 |
奥氮平
CAS:132539-06-1 |
|
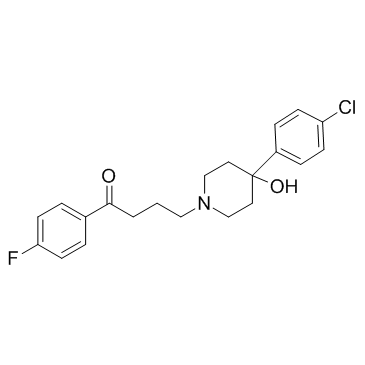 |
氟哌啶醇
CAS:52-86-8 |