| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|
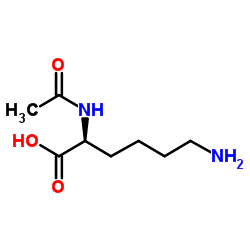 |
Nα-乙酰-L-赖氨酸
CAS:1946-82-3 |
|
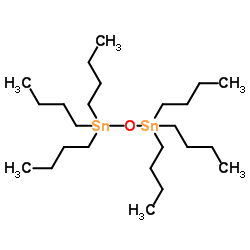 |
三丁基氧化锡
CAS:56-35-9 |
|
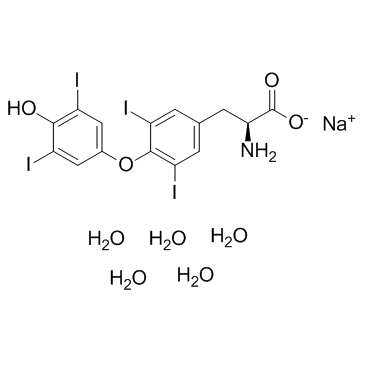 |
L-甲状腺素钠五水合物(左甲状腺素钠)
CAS:6106-07-6 |