| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|
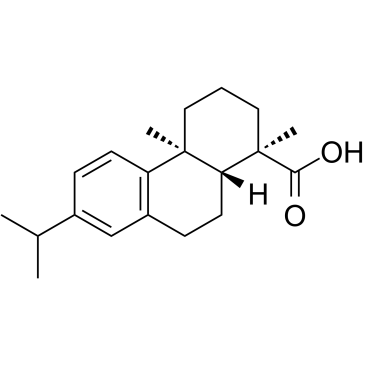 |
脱氢枞酸; 脱氢松香酸
CAS:1740-19-8 |
|
 |
山梨醇脱氢酶(微生物)
CAS:9028-21-1 |