| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|
 |
镉
CAS:7440-43-9 |
|
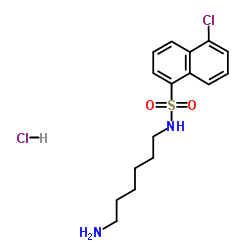 |
N-(6-氨基己基)-5-氯-1-萘磺酰胺盐酸盐
CAS:61714-27-0 |
|
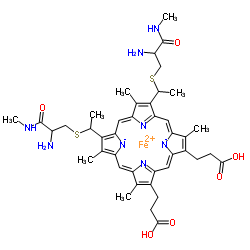 |
细胞色素C
CAS:9007-43-6 |
|
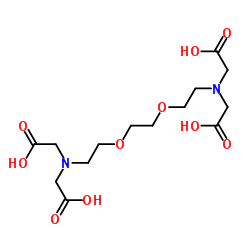 |
3,6-二氧杂-1,8-辛二胺四乙酸(EGTA)
CAS:67-42-5 |