| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|
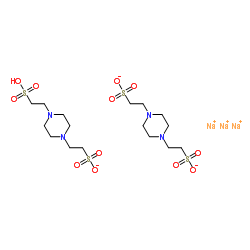 |
哌嗪-1,4-二乙磺酸
CAS:5625-37-6 |
|
 |
4-羟乙基哌嗪乙磺酸
CAS:7365-45-9 |
|
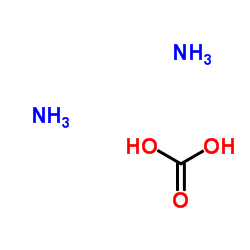 |
碳酸铵
CAS:506-87-6 |