Crystal structures of Paenibacillus polymyxa beta-glucosidase B complexes reveal the molecular basis of substrate specificity and give new insights into the catalytic machinery of family I glycosidases.
Pablo Isorna, Julio Polaina, Lorena Latorre-García, Francisco Javier Cañada, Beatriz González, Julia Sanz-Aparicio
文献索引:J. Mol. Biol. 371 , 1204-1218, (2007)
全文:HTML全文
摘要
Bacteria species involved in degradation of cellulosic substrates produce a variety of enzymes for processing related compounds along the hydrolytic pathway. Paenibacillus polymyxa encodes two homologous beta-glucosidases, BglA and BglB, presenting different quaternary structures and substrate specificities. We previously reported the 3D-structure of BglA, which is highly specific against cellobiose. Here, we present structural analysis of BglB, a monomeric enzyme that acts as an exo-beta-glucosidase hydrolyzing cellobiose and cellodextrins of higher degree of polymerization. The crystal structure of BglB shows that several polar residues narrow the active site pocket and contour additional subsites. The structure of the BglB-cellotetraose complex confirms these subsites, revealing the substrate-binding mode, and shows the oligosaccharide-enzyme recognition pattern in detail. Comparison between BglA and BglB crystal structures suggests that oligomerization in BglA can assist in fine-tuning the specificity of the active centre by modulating the loops surrounding the cavity. We have solved the crystal structure of BglB with bound thiocellobiose, a competitive inhibitor, which together with the BglB-cellotetraose complex delineate the general features of the aglycon site. The detailed characterization of the atomic interactions at the aglycon site show a recognition pattern common to all bacterial beta-glucosidases, and presents some differences with the aglycon site in plant beta-glycosidases essentially by means of a different orientation of the basal Trp. The crystal structures of of BglB with a covalently bound inhibitor (derived from 2-fluoroglucoside) and glucose (produced by hydrolysis of the substrate in the crystal), provide additional pictures of the binding events and the intermediates formed during the reaction. Altogether, this information can assist in the understanding of subtle differences of the enzyme mechanism and substrate recognition within this family of enzymes, and consequently it can help in the development of new enzymes with improved activity or specificity.
相关化合物
| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 分子式 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|---|
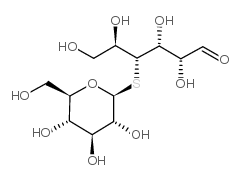 |
硫代纤维二糖
CAS:80951-92-4 |
C12H22O10S |
|
Substrate specificity of cellobiose dehydrogenase from Phane...
1998-03-03 [Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1383 , 48-54, (1998)] |
|
Purification and characterization of cellobiose dehydrogenas...
2001-04-01 [Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 67 , 1766-1774, (2001)] |
|
NMR studies of the conformation of thiocellobiose bound to a...
1998-01-16 [FEBS Lett. 421 , 243-248, (1998)] |
|
Induction of cellulose in Schizophyllum commune: thiocellobi...
1982-01-01 [J. Bacteriol. 149 , 47, (1982)] |
|
Alleviating product inhibition in cellulase enzyme Cel7A.
2016-02-01 [Biotechnol. Bioeng. 113 , 330-8, (2016)] |