Removal of copper, chromium and arsenic from preservative-treated wood by chemical extraction-fungal bioleaching.
Reyes Sierra-Alvarez
文献索引:Waste Manag. 29(6) , 1885-91, (2009)
全文:HTML全文
摘要
Large volumes of preservative-treated wood containing toxic Cr, Cu and As salts are decommissioned worldwide. This study investigated the effectiveness of solid-state fermentation with copper-tolerant brown-rot fungi for the remediation of wood treated with chromated copper arsenate (CCA) and acid copper chromate (ACC) formulations. Treatment of CCA- and ACC-wood with the most effective strain, Antrodia vaillantii FRLP-14G, attained extensive leaching of As and/or Cr, but Cu elimination was poor (<18%). Additional research showed that a variety of organic acids, including citrate, are effective Cu extractants. Based on these findings, a process combining chemical extraction and subsequent fungal treatment was developed that proved highly effective in removing inorganic pollutants from CCA-wood. Extraction of CCA-wood with citric acid (30 mM, pH 3.10) followed by a 28-day solid-state fermentation period removed 87% Cu, 80% Cr, and 100% As. These results indicate the potential of the two-stage process for the remediation of preservative-treated wood.
相关化合物
| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 分子式 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|---|
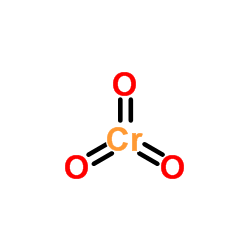 |
铬酸酐
CAS:1333-82-0 |
CrO3 |
|
Impairment of renal structure and function following heterog...
2014-04-01 [Indian J. Exp. Biol. 52(4) , 332-43, (2014)] |
|
[Improved methodology for quantitative determination of thia...
2012-01-01 [Kokuritsu Iyakuhin Shokuhin Eisei Kenkyusho. Hokoku. (130) , 46-9, (2012)] |
|
Genotoxicity of tri- and hexavalent chromium compounds in vi...
2014-01-01 [PLoS ONE 9(8) , e103194, (2014)] |
|
Carbohydrate utilization by tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus x...
1993-10-01 [J. Nutr. 123(10) , 1747-53, (1993)] |
|
Arsenite and cadmium, but not chromium, induce NAD(P)H:quino...
2008-08-01 [Toxicol. In Vitro 22(5) , 1184-90, (2008)] |