| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|
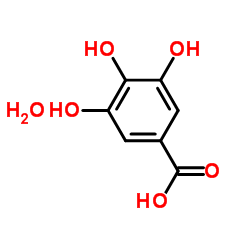 |
没食子酸水合物
CAS:5995-86-8 |
|
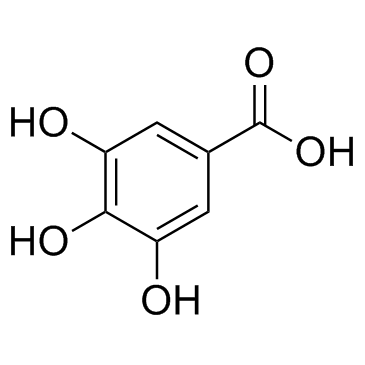 |
没食子酸; 3,4,5-三羟基苯甲酸
CAS:149-91-7 |
|
 |
丁香酸
CAS:530-57-4 |
|
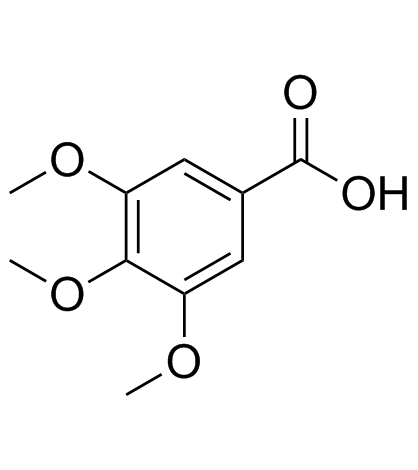 |
3,4,5-三甲氧基苯甲酸
CAS:118-41-2 |
|
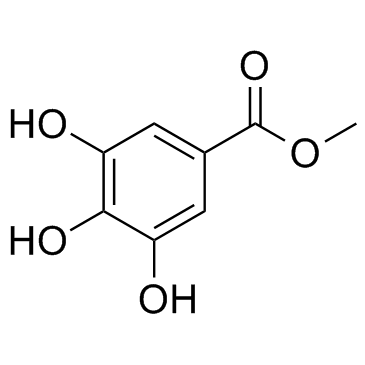 |
没食子酸甲酯
CAS:99-24-1 |