| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|
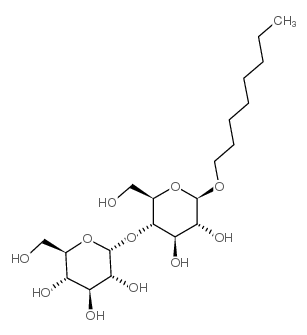 |
正辛基-β-D-麦芽糖苷
CAS:82494-08-4 |
|
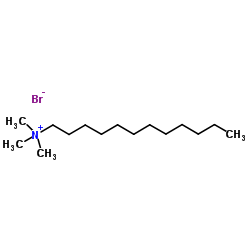 |
十二烷基三甲基溴化铵
CAS:1119-94-4 |
|
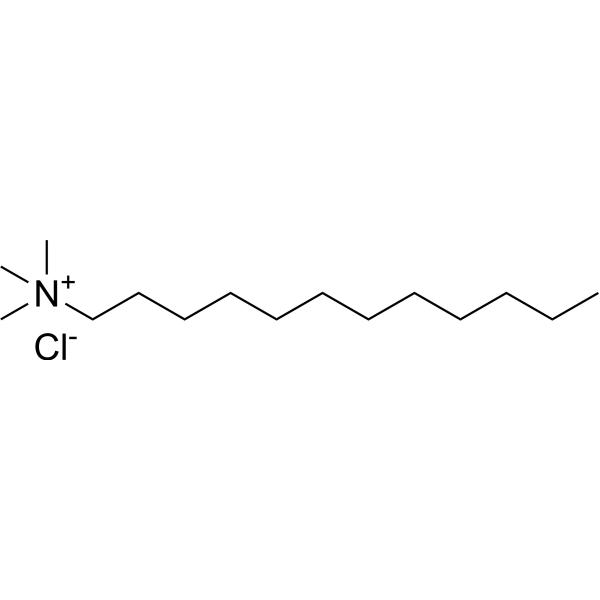 |
十二烷基三甲基氯化铵
CAS:112-00-5 |