| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|
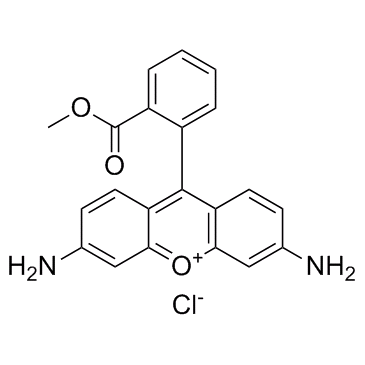 |
罗丹明123
CAS:62669-70-9 |
|
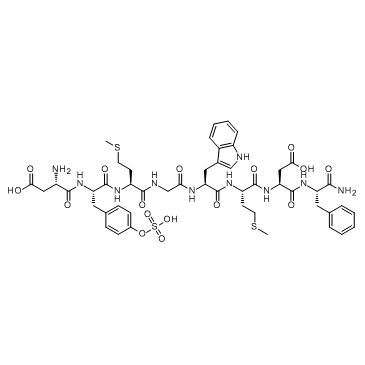 |
辛卡利特
CAS:25126-32-3 |
|
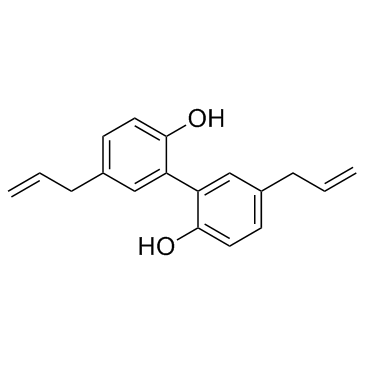 |
厚朴酚
CAS:528-43-8 |