A systematic study on spatial and seasonal patterns of eight taste and odor compounds with relation to various biotic and abiotic parameters in Gonghu Bay of Lake Taihu, China.
Jun Chen, Ping Xie, Zhimei Ma, Yuan Niu, Min Tao, Xuwei Deng, Qing Wang
文献索引:Sci. Total Environ. 409(2) , 314-25, (2010)
全文:HTML全文
摘要
A systematic study was conducted on seasonal and spatial patterns of taste and odor (T&O) compounds with relation to biotic and abiotic parameters at fifteen sites in Gonghu Bay of Lake Taihu in 2008. We developed a sensitive and automated method to simultaneously analyze eight T&O compounds (boiling points ranging from 38°C to 239°C) by using Purge-and-Trap (P&T) coupled with GC/MS. Maximum particulate dimethyl trisulfide (DMTS, 69.6 ng/L) exceeded its odor threshold concentrations (OTC, 10 ng/L) and maximum dissolved DMTS was 6.1 ng/L, but still far below concentration in the drinking water pollution incident of Wuxi City in 2007 when DMTS reached 1768-11,399 ng/L. Geosmin (GEO), 2-methylisoborneol (MIB), β-cyclocitral, β-ionone and 2-isobutyl-3-methoxypyrazine (IBMP) occasionally or frequently exceeded their OTCs, whereas 2-isopropyl-3-methoxypyrazine (IPMP) and dimethyl sulfide (DMS) did not. We found for the first time significant correlations between particulate β-cyclocitral and β-ionon concentrations and intracellular and extracellular microcystin concentrations. Spatially, Nanquan Waterworks faced more risk by T&O contamination than Xidong Waterworks. High concentrations of NO(3)-N, TDN and TN could be risky signs of taste and odor events by DMS, DMTS, IPMP, IBMP and GEO.Copyright © 2010 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
相关化合物
| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 分子式 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|---|
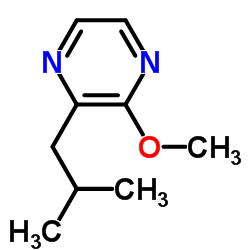 |
2-甲氧基-3-异丁基吡嗪
CAS:24683-00-9 |
C9H14N2O |
|
Dynamics of odorant binding to thin aqueous films of rat-OBP...
2011-09-01 [Chem. Senses 36(7) , 659-71, (2011)] |
|
Occurrence of dissolved and particle-bound taste and odor co...
2009-05-01 [Water Res. 43(8) , 2191-200, (2009)] |
|
Rapid measurement of 3-alkyl-2-methoxypyrazine content of wi...
2009-09-23 [J. Agric. Food Chem. 57(18) , 8250-7, (2009)] |
|
Automated trace determination of earthy-musty odorous compou...
2006-12-15 [J. Chromatogr. A. 1136(2) , 170-5, (2006)] |
|
Development of a mixed-mode solid phase extraction method an...
2011-02-11 [J. Chromatogr. A. 1218(6) , 842-8, (2011)] |