| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|
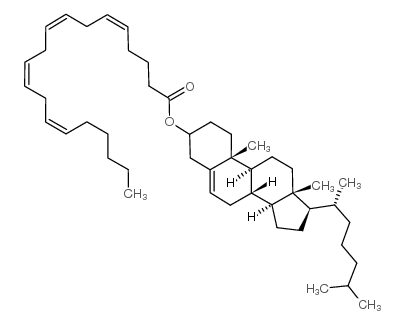 |
花生四烯酸胆固醇
CAS:604-34-2 |
|
 |
胆固醇山酸酯
CAS:61510-09-6 |
|
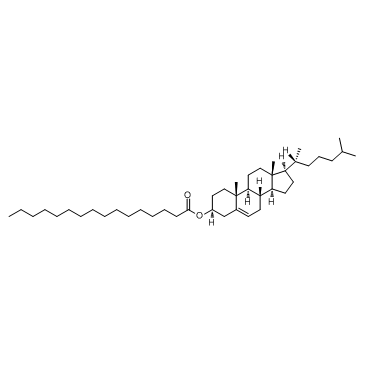 |
棕榈酸胆固醇酯
CAS:601-34-3 |
|
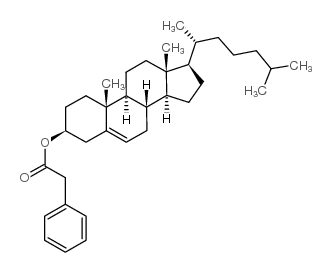 |
苯乙酸胆固醇酯
CAS:33998-26-4 |