Effects of nicergoline on corneal epithelial wound healing in rat eyes.
Su-Young Kim, Jun-Sub Choi, Choun-Ki Joo
文献索引:Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 50(2) , 621-5, (2009)
全文:HTML全文
摘要
To investigate the effect of nicergoline on corneal epithelial wound healing in rats.One hundred Sprague-Dawley male rats were divided into two groups, the control group and the nicergoline-treated group, for 2 weeks. Corneal wound healing was evaluated by fluorescein staining after epithelial debridement. Nerve growth factor (NGF) protein and NGF mRNA were measured in rat corneas by ELISA and RT-PCR. NGF concentration of lacrimal gland was also evaluated by means of ELISA. Immunofluorescent staining was performed in rat corneas.The corneal wound healing rate was increased in nicergoline-treated rats compared with control rats after debridement. Twenty-four hours after epithelial debridement, corneal NGF protein and NGF mRNA levels were higher in the nicergoline-treated group than in the control group. Immunofluorescent staining showed that NGF staining was stronger in nicergoline-treated corneas than in control corneas 24 hours after epithelial debridement. In addition, NGF concentrations in lacrimal glands of the nicergoline-treated group were significantly higher than in the control group 24 hours after epithelial debridement.Nicergoline accelerated wound healing in rat corneas. The promoting effect of nicergoline in corneal wound healing is likely to be related to increased NGF in corneas and lacrimal glands.
相关化合物
| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 分子式 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|---|
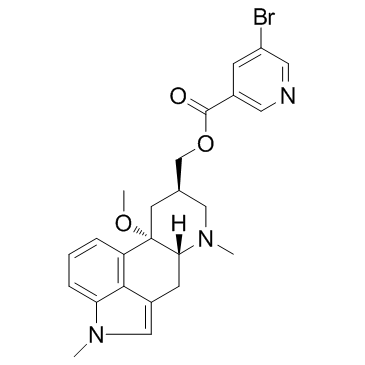 |
尼麦角林
CAS:27848-84-6 |
C24H26BrN3O3 |
|
Structural alteration of cell surface heparan sulfate throug...
2014-01-01 [Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 78(5) , 770-9, (2014)] |
|
[Nicergoline, ibudilast, ifenprodil tartrate].
2006-10-28 [Nihon Rinsho. 64 Suppl 7 , 602-5, (2006)] |
|
Protective effects of nicergoline against neuronal cell deat...
2005-12-20 [Brain Res. 1066(1-2) , 78-85, (2005)] |
|
Smart stability-indicating spectrophotometric methods for de...
2008-01-01 [J. AOAC Int. 91(2) , 299-310, (2008)] |
|
Wakayama symposium: new therapies for modulation of epitheli...
2013-01-01 [Ocul. Surf. 11(1) , 16-8, (2013)] |