| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|
 |
腺苷高半胱氨酸水解酶
CAS:9025-54-1 |
|
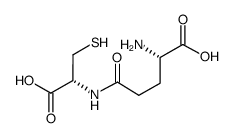 |
G-谷氨酸-半胱-三氟乙酸盐
CAS:636-58-8 |