| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|
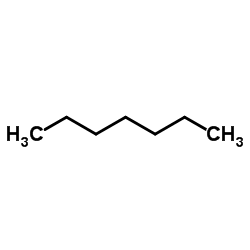 |
正庚烷
CAS:142-82-5 |
|
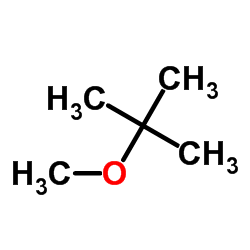 |
甲基叔丁基醚
CAS:1634-04-4 |
|
 |
乙基叔丁基醚
CAS:637-92-3 |
|
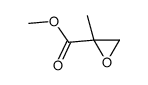 |
2-甲基缩水甘油酸甲酯
CAS:58653-97-7 |