| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|
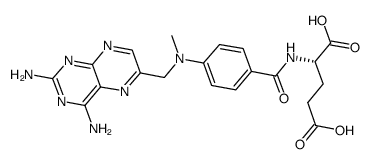 |
二水合氨甲嘌呤
CAS:133073-73-1 |
|
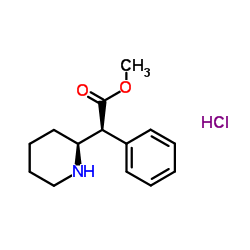 |
盐酸哌甲酯
CAS:298-59-9 |
|
 |
莫达非尼
CAS:68693-11-8 |
|
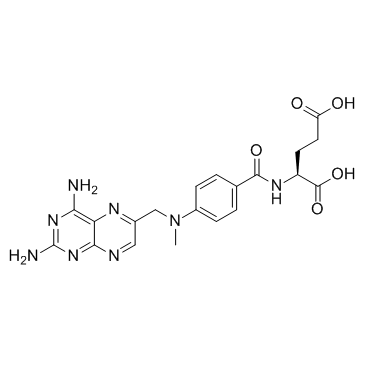 |
甲氨蝶呤
CAS:59-05-2 |
|
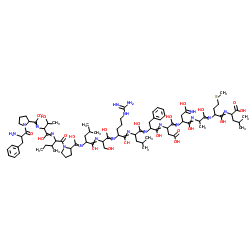 |
人生长激素
CAS:12629-01-5 |