Effects of selective oral antimicrobial prophylaxis and systemic antibiotics on the fecal flora and fecal beta-aspartylglycine concentration in patients with acute leukemia.
W Bär, G W Welling, E Kurrle
文献索引:APMIS 97(8) , 705-14, (1989)
全文:HTML全文
摘要
The influence of selective oral antimicrobial prophylaxis (SOAP) and systemic antibiotic treatment (SAT) on the intestinal flora of fourteen granulocytopenic patients was investigated. For SOAP, patients received Cotrimoxazole, Polymyxin and Nystatin; Gentamicin, Ticarcillin and Cefuroxime were administered for SAT. Under SOAP, a complete elimination of Enterobacteriaceae and a marked reduction of yeasts and staphylococci was found. A reduction in the number of anaerobic species was also observed; however, the concentration of anaerobic bacteria remained constant. In contrast, additional systemic antibiotic treatment caused a significant reduction of aerobic as well as anaerobic bacteria, except for microorganisms pathogenic to neutropenic patients (i.e. Staphylococcus epidermidis and Candida sp.). The fecal concentration of beta-aspartylglycine was inversely correlated with the presence of anaerobic bacteria.
相关化合物
| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 分子式 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|---|
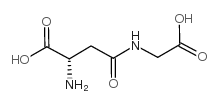 |
Beta-天冬氨酰甘氨酸
CAS:3790-52-1 |
C6H10N2O5 |
|
'Normalization' of germfree mice after direct and indirect c...
1986-10-01 [Lab. Anim. 20(4) , 286-90, (1986)] |
|
Influence of zinc bacitracin and Bacillus licheniformis on m...
2003-10-01 [Vet. Res. Commun. 27(7) , 513-26, (2003)] |
|
[Rapid diagnosis of dysbacteriosis by detecting beta-asparty...
1985-08-01 [Zh. Mikrobiol. Epidemiol. Immunobiol. (8) , 15-8, (1985)] |
|
[Changes in the microflora of the large intestine in rats ad...
1987-03-01 [Antibiot. Med. Biotekhnol. 32(3) , 206-10, (1987)] |
|
Identification of an acidic dipeptide, beta-aspartylglycine,...
1984-11-01 [J. Neurochem. 43(5) , 1375-84, (1984)] |