Stereoselective isomerisation of N-allyl aziridines into geometrically stable Z enamines by using rhodium hydride catalysis.
Derek S Tsang, Sharon Yang, France-Aimée Alphonse, Andrei K Yudin
文献索引:Chemistry 3rd ed., 14 , 886-894, (2008)
全文:HTML全文
摘要
In the presence of rhodium(I) hydride catalysts, tertiary N-allylamines are known to isomerise into E enamines. In contrast, we have recently found that N-allylaziridines isomerise to form Z enamines. On the basis of literature data, the most likely mechanism of isomerisation would involve a rhodium hydride addition/beta-hydride elimination sequence. We show that the observed selectivity cannot be adequately explained by this pathway and is more consistent with initial CH-activation followed by rearrangement to form a five-membered cyclometallated rhodium intermediate. This intermediate subsequently undergoes reductive elimination to form a C--H bond. The resulting geometrically stable Z enamines are useful building blocks for stereoselective synthesis.
相关化合物
| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 分子式 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|---|
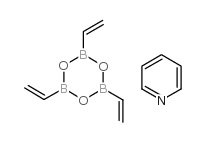 |
乙烯硼酐吡啶络合物
CAS:442850-89-7 |
C11H14B3NO3 |
|
Transition metal-catalyzed synthesis and reactivity of N-alk...
2005-03-17 [Org. Lett. 6th ed., 7 , 1161-1164, (2005)] |
|
The alkyl-connected 2-amino-6-vinylpurine (AVP) crosslinking...
2010-01-01 [Bioorg. Med. Chem. 8th ed., 18 , 2894-2901, (2010)] |
|
Kinetic resolution of axially chiral 2,2'-dihydroxy-1,1'-bia...
2005-08-03 [J. Am. Chem. Soc. 30th ed., 127 , 10474-10475, (2005)] |
|
Efforts toward distorted spiropentanes.
2010-11-05 [J. Org. Chem. 21th ed., 75 , 7494-7497, (2010)] |
|
Structure based design, synthesis and SAR of cyclic hydroxye...
2011-04-01 [Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 7th ed., 21 , 1942-1947, (2011)] |